Storage Account
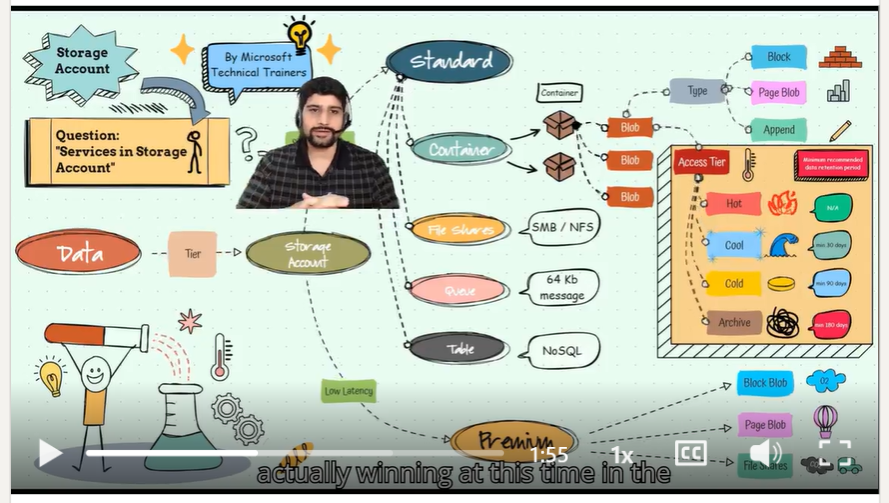
Above illustrates the process of using an Azure Storage Account. We start by understanding the pricing tiers and the various services it offers. Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
- Pricing Tier: Choose the appropriate pricing tier based on your needs. Azure Storage offers different tiers to optimize cost and performance 💰.
- Services: Azure Storage provides several services to store different types of data:
- Blob Storage: For storing large amounts of unstructured data 📦.
- File Storage: Managed file shares for cloud or on-premises deployments 📁.
- Table Storage: NoSQL key-value store for rapid development 📋.
- Queue Storage: Messaging queue for communication between application components 📬.
- Blob Types: Understand the different types of blobs available:
- Block Blobs: For storing text and binary data 📝.
- Append Blobs: Optimized for append operations, such as logging 📜.
- Page Blobs: For random read/write operations, often used for virtual hard disks 💾.
- Access Tiers: Select the appropriate access tier based on how frequently you need to access the data:
- Hot: For data that is accessed frequently 🔥.
- Cool: For data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days ❄️.
- Cold: For data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 90 days 🧊.
- Archive: For data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days 🗄️.
⚠️ Penalties
Be aware of the penalties associated with moving data between access tiers. For example, moving data from the Archive tier to the Hot tier may incur additional costs.
🎬 Video Explanation
Click the video below for recorded explanations by Neeraj Kumar.