Managed Identities in Azure: Enhancing Security Part 2
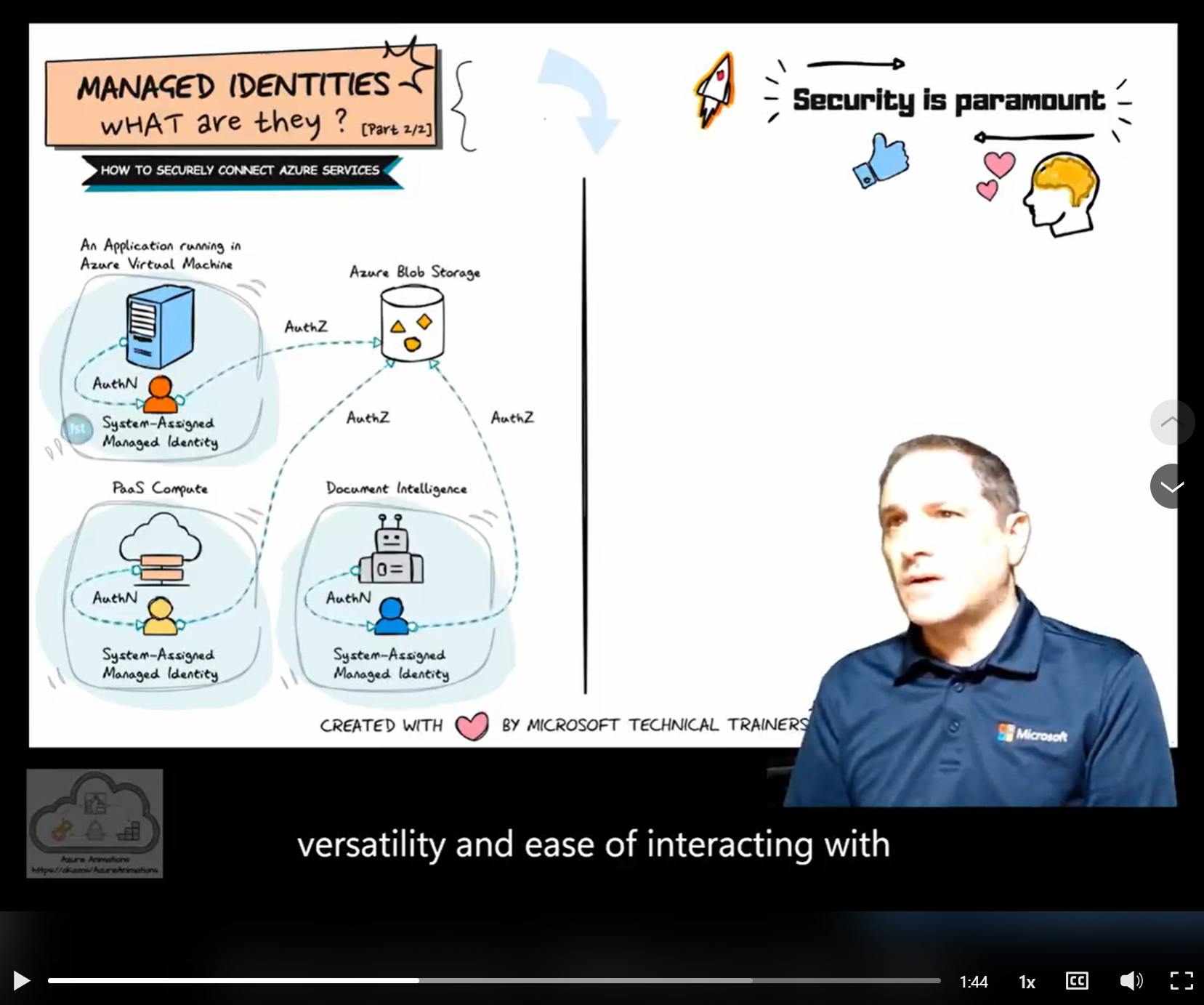
The animation on the left illustrates the use of system-assigned managed identities in various scenarios:
-
Application Running in a VM 🖥️
- A system-assigned managed identity is created and tied to the VM.
- This identity is used to securely access Azure resources like Azure Blob Storage.
-
PaaS Compute Services ☁️
- PaaS compute services, such as Azure App Service or Azure Functions, each have their own system-assigned managed identity.
- These identities are automatically managed by Azure and can be used to access other Azure resources securely.
-
Document Intelligence 📄
- Document intelligence services also utilize system-assigned managed identities.
- Each service has its own identity, ensuring secure and streamlined access to necessary resources.
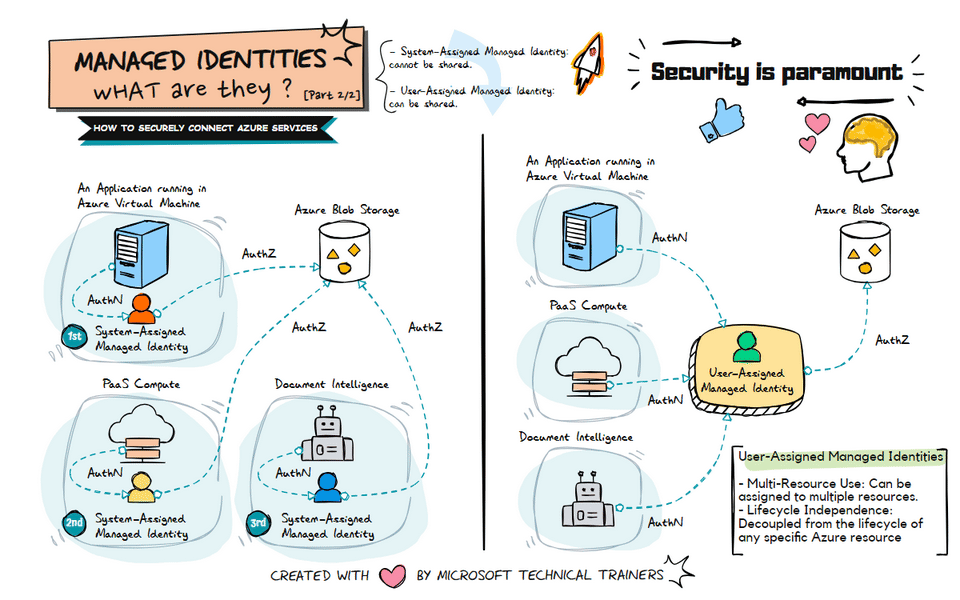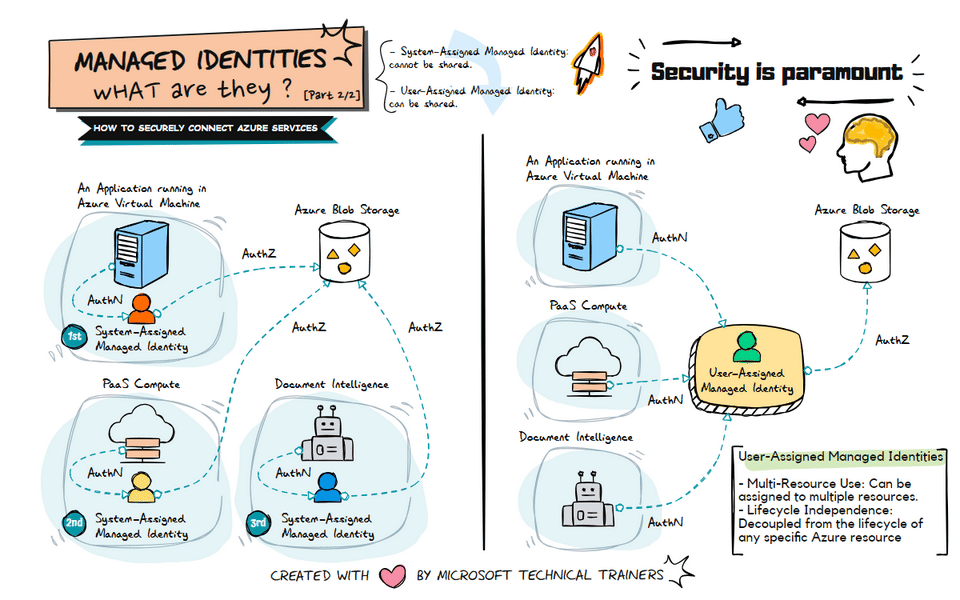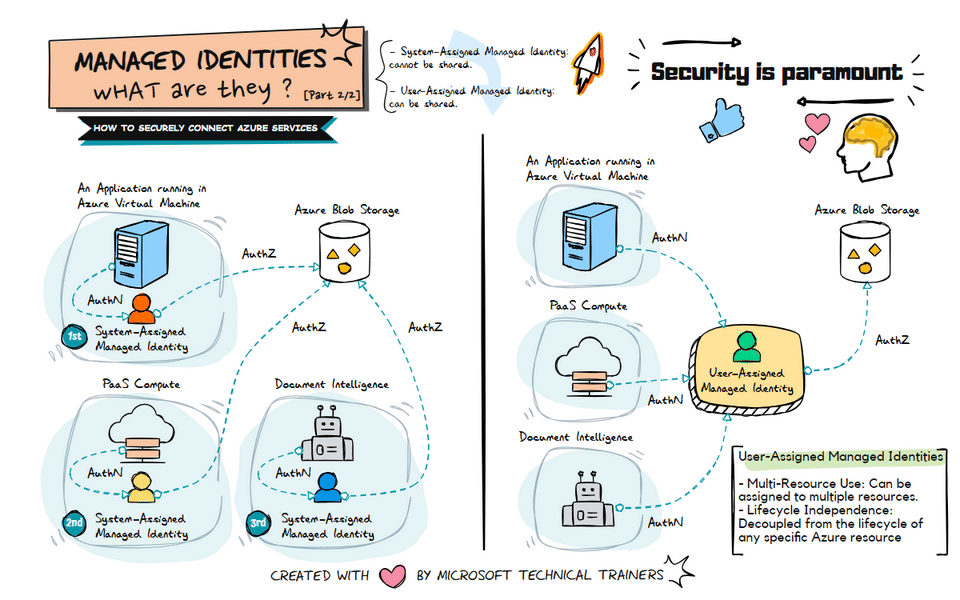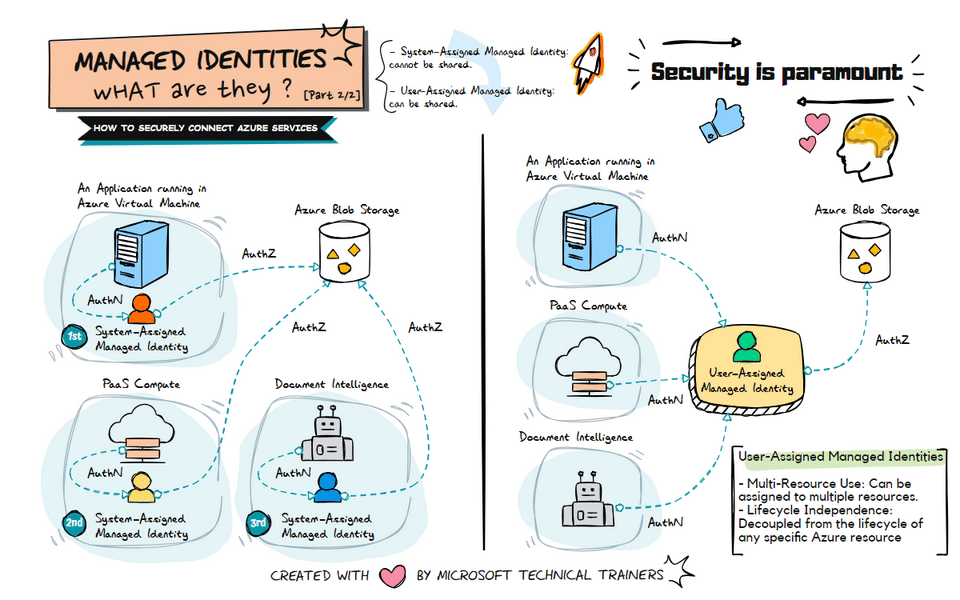
The animation on the right illustrates the use of user-assigned managed identities:
-
Shared Identity Across Multiple Resources 🔄
- A user-assigned managed identity can be created and assigned to multiple Azure resources.
- This identity can be shared among different services, such as VMs, PaaS compute services, and Document Intelligence.
-
Centralized Identity Management 🛠️
- User-assigned managed identities provide a centralized way to manage identities.
- This approach simplifies the management of permissions and access controls across multiple resources.
-
Flexible and Reusable 🔄
- User-assigned managed identities are flexible and can be reused across different resources.
- This reduces the need to create multiple identities for different services, streamlining identity management.
-
Key Points
- Automatic Identity Management: Each Azure resource (VM, PaaS compute, Document Intelligence) gets its own system-assigned managed identity.
- Secure Resource Access: These identities can be used to connect to Azure Blob Storage without managing credentials.
- Isolation and Security: Each identity is tied to a specific resource, enhancing security and isolation.
-
Example Use Case 💡
-
Azure Blob Storage Access:
- The application in the VM, PaaS compute services, and Document Intelligence services each use their respective system-assigned managed identities.
- These identities are granted the necessary permissions (RBAC) to access Azure Blob Storage.
- This setup ensures secure and seamless access to storage without the need for managing secrets.
-
Shared Identity for Multiple Resources:
- A user-assigned managed identity is created and assigned to the VM, PaaS compute services, and Document Intelligence services.
- This shared identity is granted the necessary permissions (RBAC) to access Azure Blob Storage.
- This approach simplifies identity management and provides a flexible way to manage access across multiple resources.
-
-
Conclusion 📈
System-assigned managed identities simplify identity management and enhance security by providing each Azure resource with its own identity. User-assigned managed identities offer flexibility and centralized management by allowing a single identity to be shared across multiple resources. Both approaches align with best practices for secure application development in Azure.
Click the video below for recorded explanations by Ilan Nyska.