Managed Identities in Azure: Enhancing Security Part 1
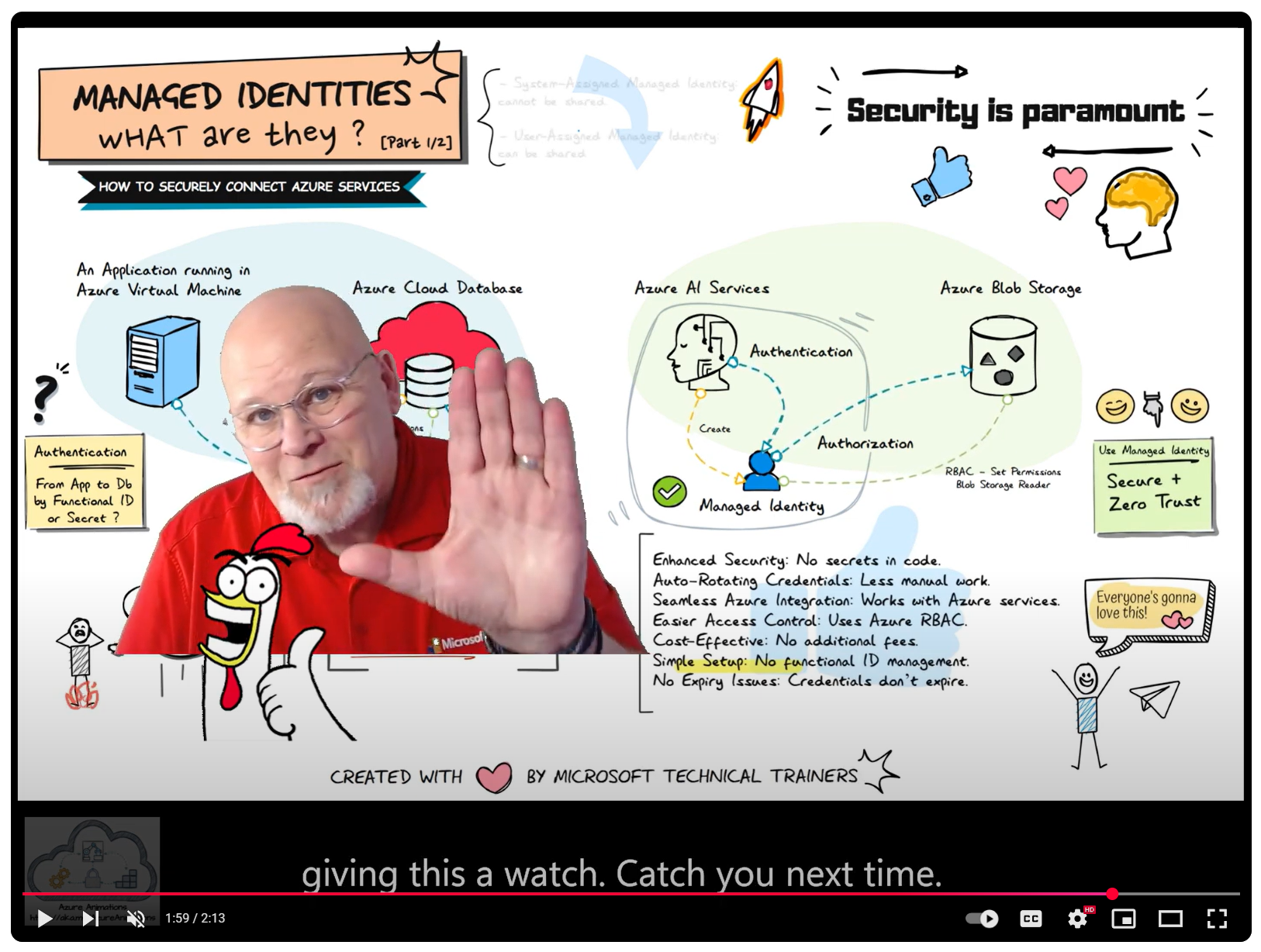
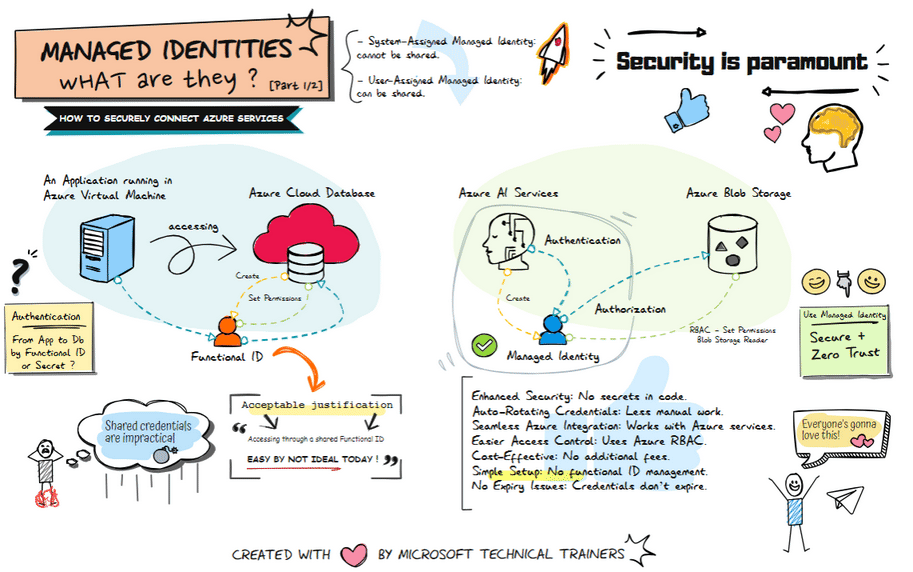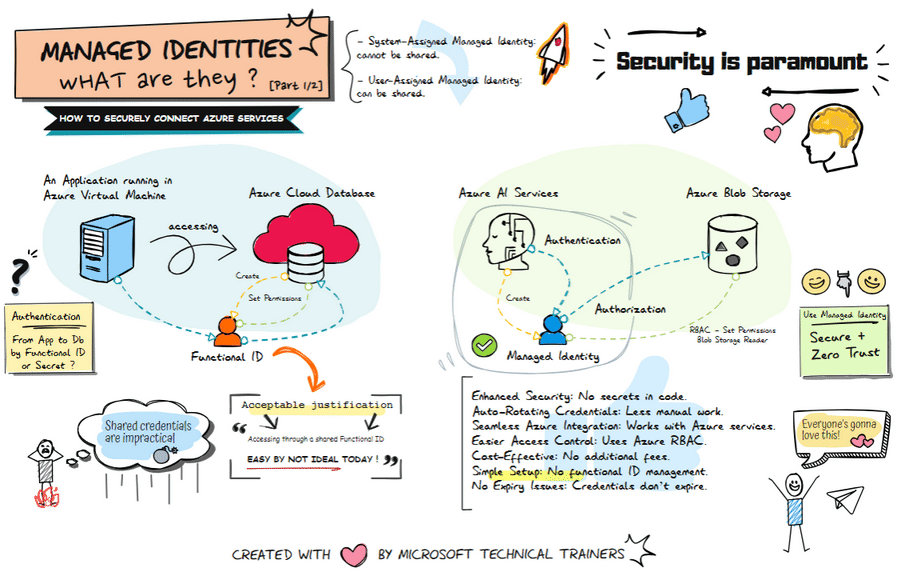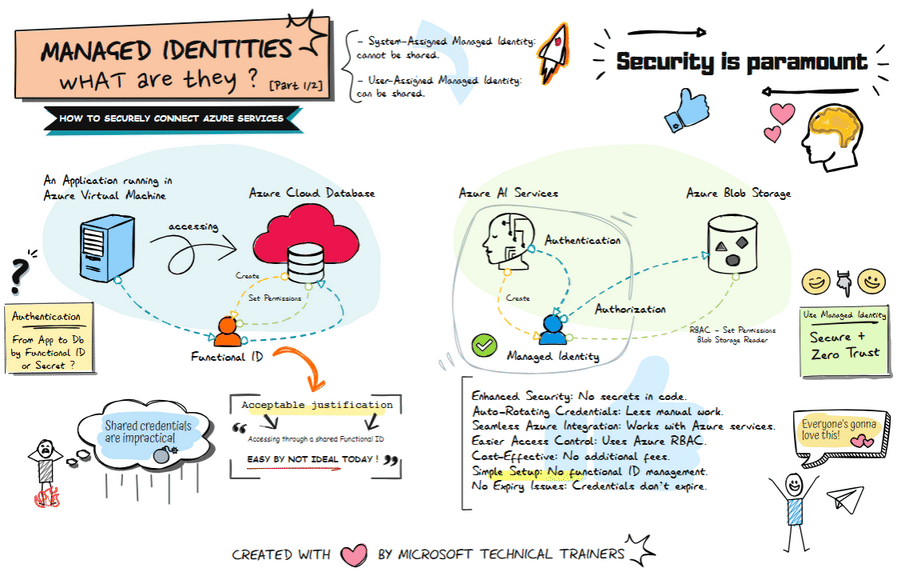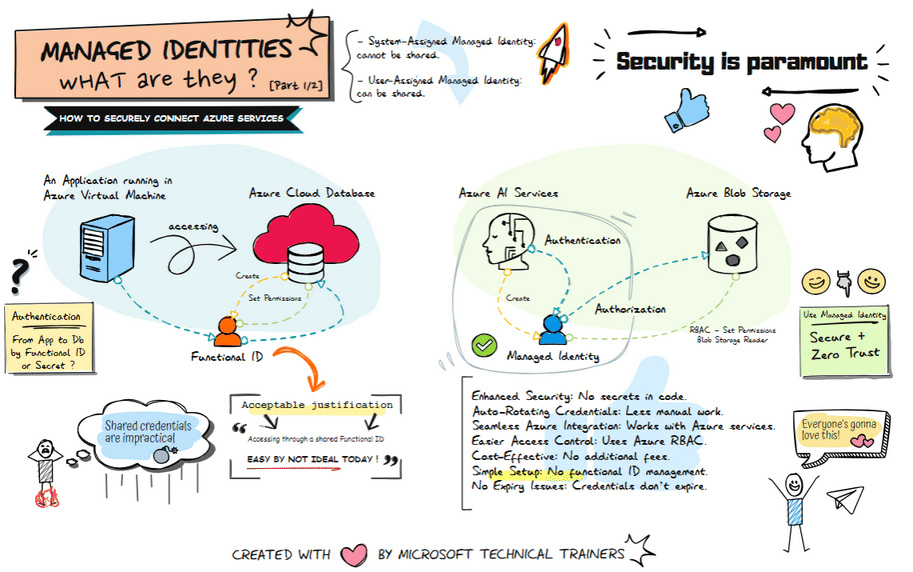
Above illustrates the process of using Managed Identities, comparing the traditional old-school way of using shared credentials to the modern approach of managed identities in Azure, highlighting enhanced security and simplified access management
-
Traditional Approach: Shared Secrets and Credentials 🔑
Using shared secrets or credentials to access Azure resources has several drawbacks:
- Security Risks: Potential exposure and misuse. ⚠️
- Maintenance Overhead: Regularly rotating secrets is cumbersome. 🔄
- Complexity: Securely distributing secrets adds complexity. 🧩
-
Modern Approach: Managed Identities in Azure 🌐
Managed identities provide a secure and streamlined way to access Azure resources without managing secrets.
-
Key Benefits 🌟
- No Secret Management: Reduces risk of exposure. 🚫🔑
- Simplified Access Control: Integrated with Azure Active Directory (AAD). 🔐
- Automatic Credential Management: Azure handles credential rotation. 🔄🔒
- Enhanced Security: Aligns with the principle of least privilege. 🛡️
-
Example Use Case 💡
Azure AI Services need to access Azure Blob Storage:
- Assigned a managed identity. 🆔
- Granted access (RBAC) to the Blob Storage. 🔐
- Authenticates and accesses data without managing credentials. 🔑
-
Conclusion 📈
Adopting managed identities enhances security, reduces overhead, and simplifies access management. This approach aligns with best practices for secure application development in Azure.
Click the video below for recorded explanations by Bob Reinsch.