Azure Virtual Network
This section covers the basics of Azure networking, including virtual machines (VMs), IP addresses, network interface cards (NICs), subnets, virtual networks (VNets), and network security groups (NSGs).
Key Concepts
Virtual Machines (VMs) 💻
- VMs: Virtual machines are the core compute resources in Azure.
IP Addresses
- Private IP Address: Used for internal communication within a VNet.
- Public IP Address: Used for communication with the internet.
Network Interface Cards (NICs) 📡
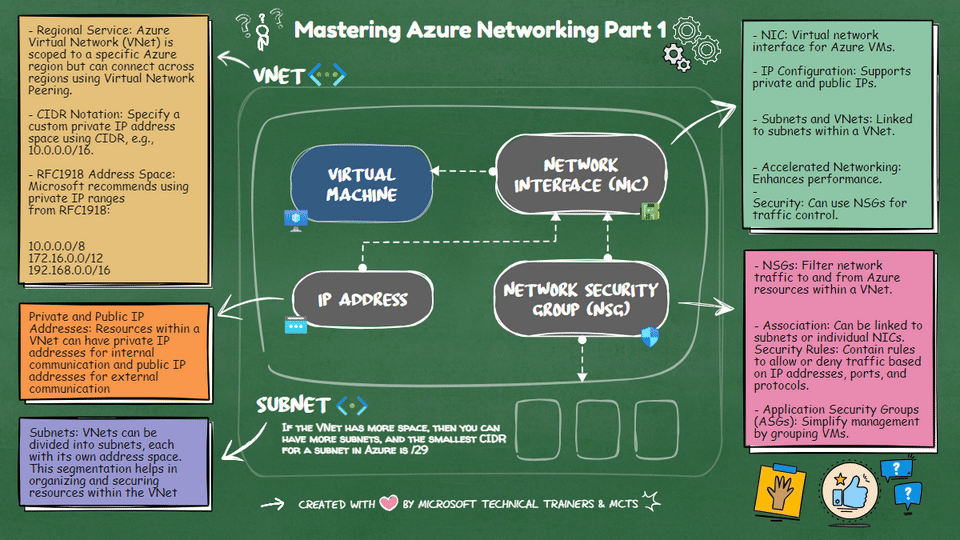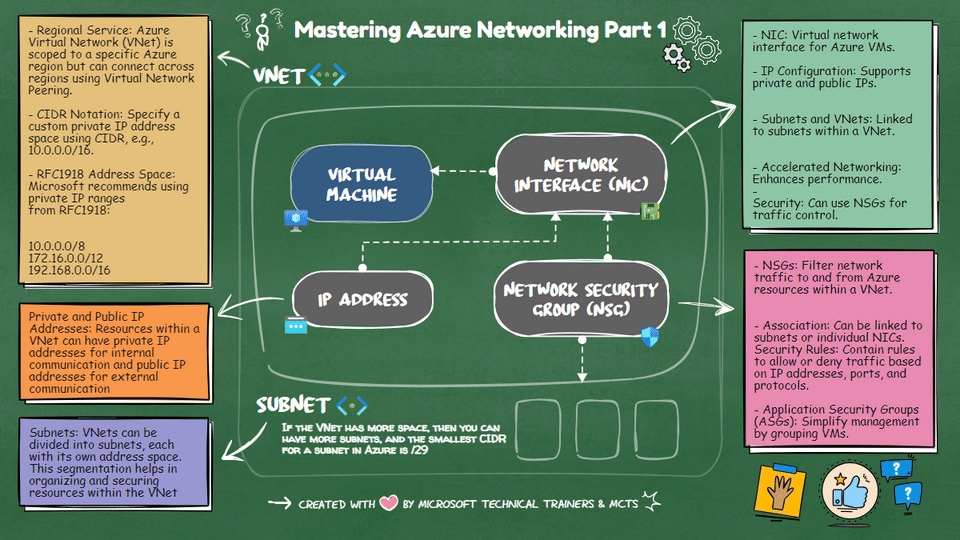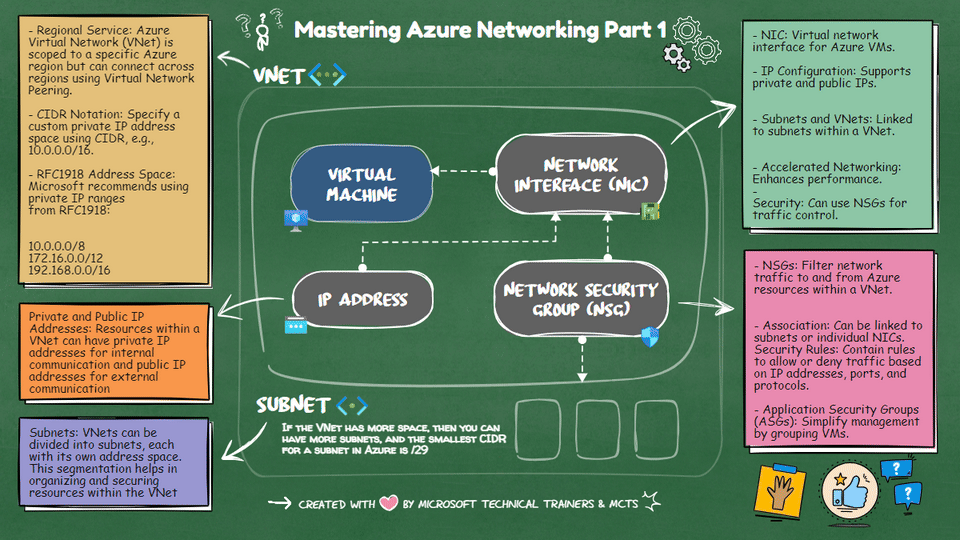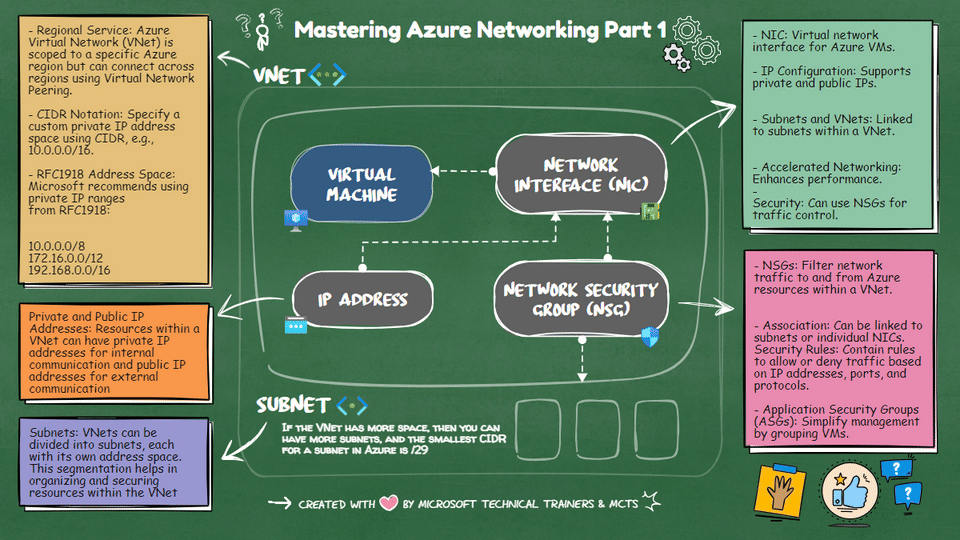
- NIC: A virtual network interface for Azure VMs.
- IP Configuration: Supports private and public IPs.
- Subnets and VNets: Linked to subnets within a VNet.
- Accelerated Networking: Enhances performance.
- Security: Can use NSGs for traffic control.
Subnets 🔗
- Subnets: Segments within a VNet to organize and secure resources.
- Smallest CIDR: The smallest CIDR for a subnet in Azure is /29.
Virtual Networks (VNets) 🌐
- Regional Service: Scoped to a specific Azure region but can connect across regions using Virtual Network Peering.
- CIDR Notation: Specify a custom private IP address space using CIDR, e.g., 10.0.0.0/16.
- RFC1918 Address Space: Microsoft recommends using private IP ranges from RFC1918:
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
Network Security Groups (NSGs) 🔒
- NSGs: Filter network traffic to and from Azure resources within a VNet.
- Association: Can be linked to subnets or individual NICs.
- Security Rules: Contain rules to allow or deny traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
- Default Rules: Include default rules with the lowest priority.
- Application Security Groups (ASGs): Simplify management by grouping VMs.
- Flow Logs: Provide information about allowed or denied traffic for monitoring.