Azure Region and Zone
Overview
Microsoft Azure is a global cloud computing platform. Understanding Regions and Availability Zones is crucial for designing resilient solutions.
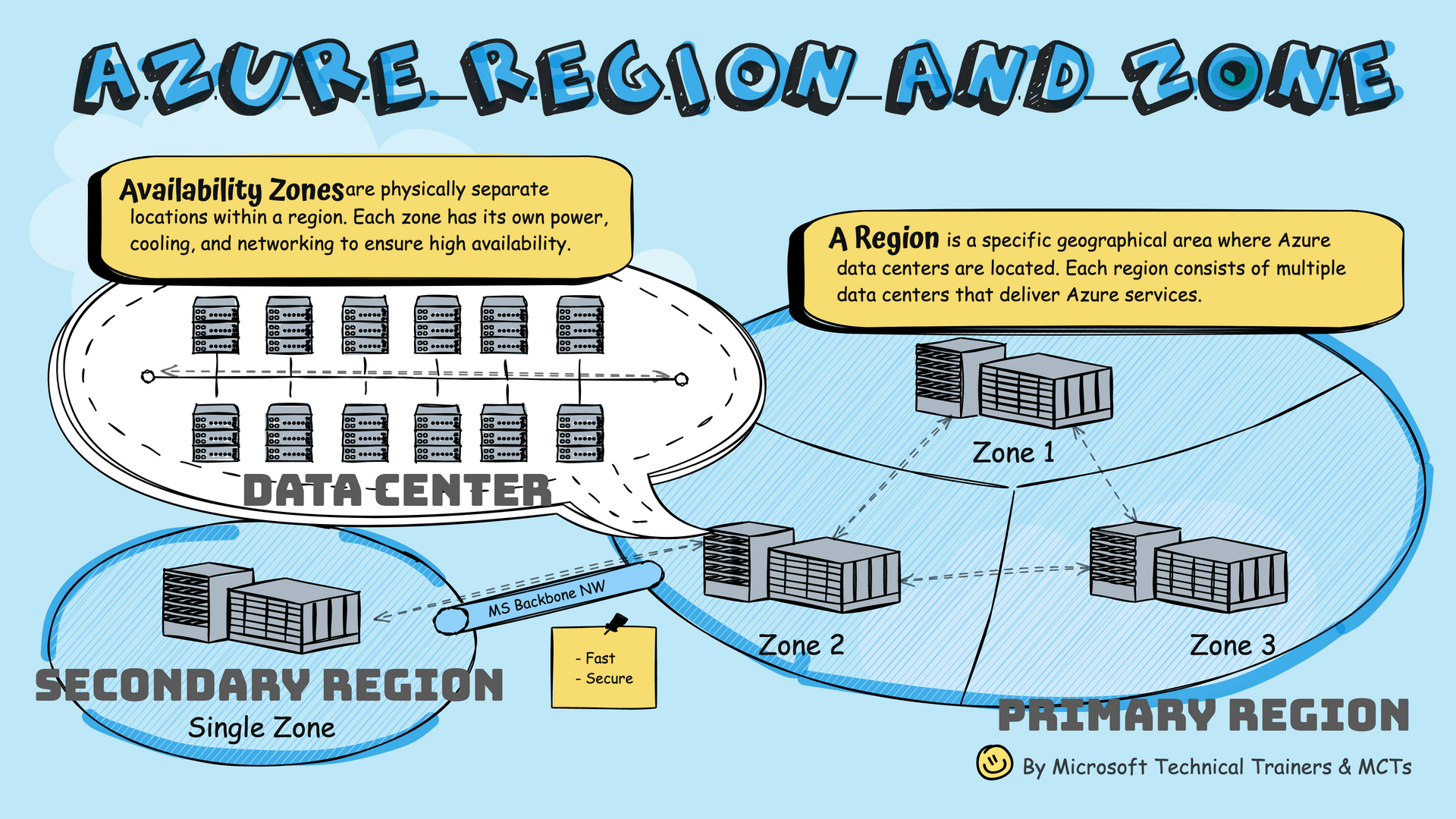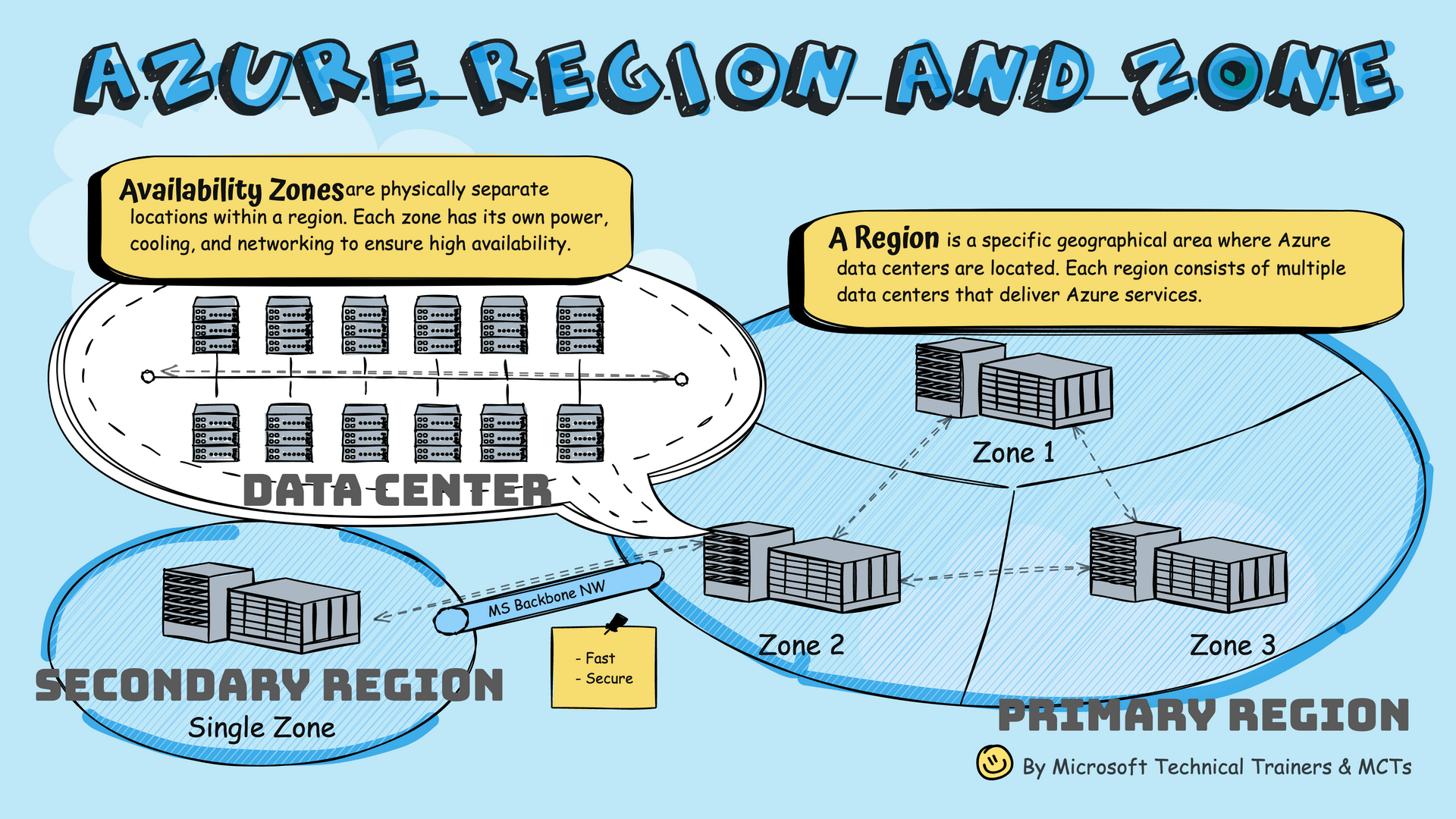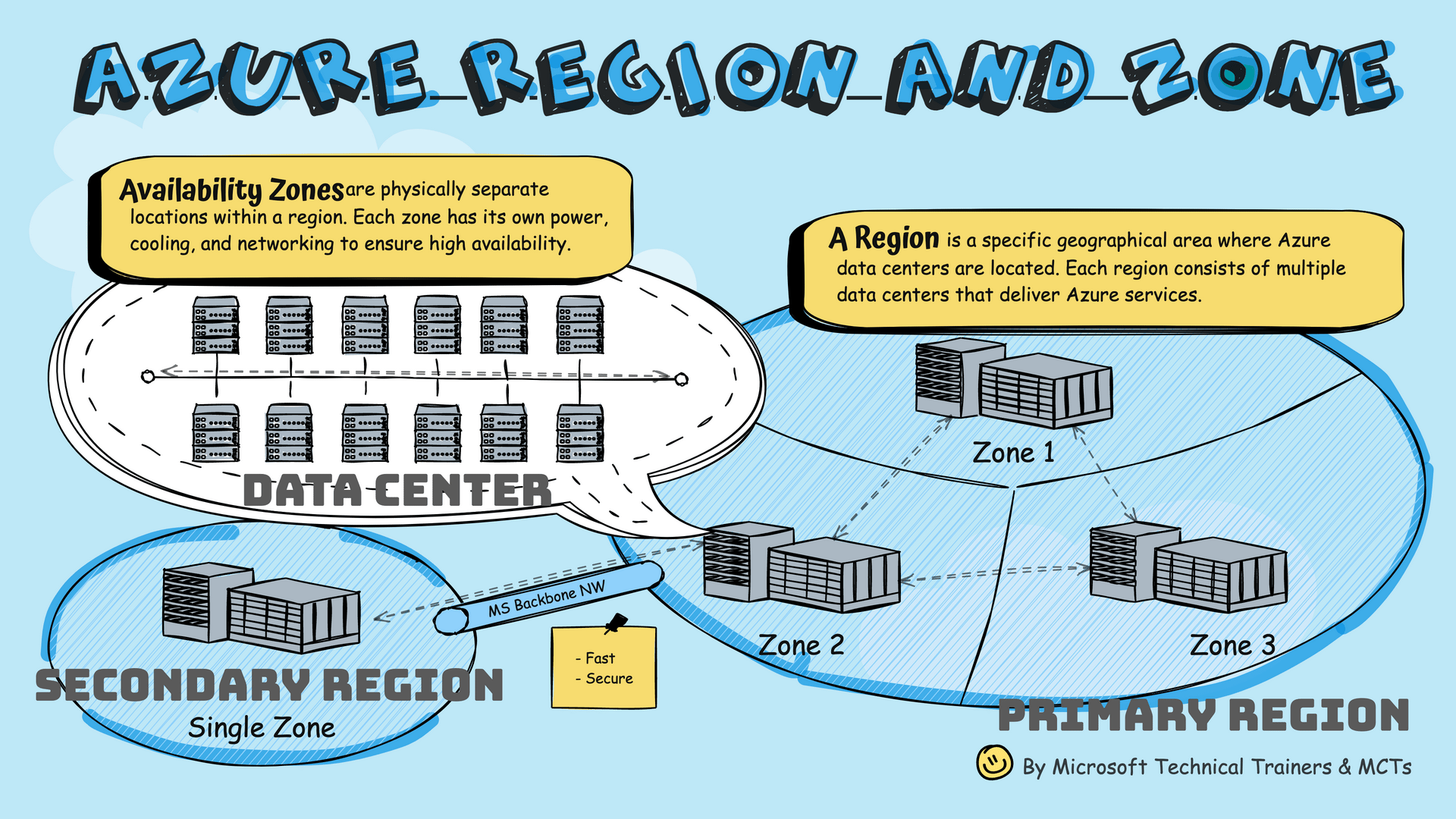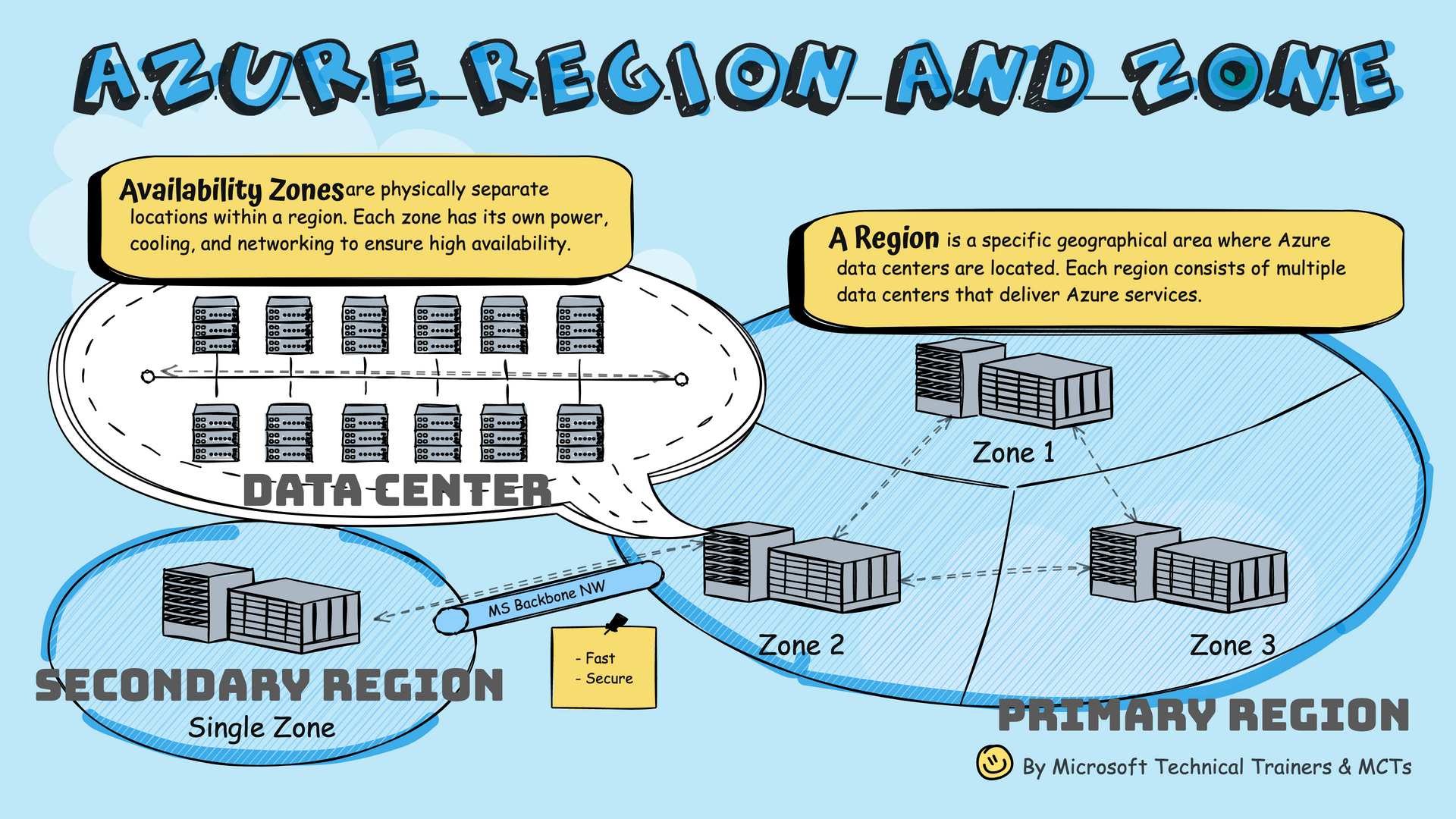
Availability Zones
Physically separate locations within a region with independent power, cooling, and networking.
Key Benefits:
- Fault Isolation: If one zone has an issue, others remain operational
- Redundancy: Deploying across multiple zones improves resilience
- Low Latency: All zones are within the same region
Region
A specific geographical area where Azure data centers are located.
Factors to Consider:
- Proximity to Users: Choose a region close to reduce latency
- Regulatory Compliance: Some regions comply with specific requirements
- Service Availability: Not all services are available in every region
Primary and Secondary Regions
- Primary Region: Contains multiple Availability Zones (Zone 1, 2, 3)
- Secondary Region: Connected via Microsoft's Backbone Network
- Geo-Redundancy: Some services offer GRS, replicating to secondary region
Best Practices
- Deploy across multiple Availability Zones
- Use Azure Traffic Manager for traffic distribution
- Implement Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Monitor latency and performance
- Ensure compliance and security requirements